Geodetic Coordinate System
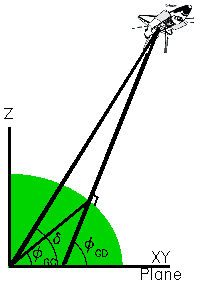
Geodetic Coordinate System.
For any selected point above
the surface of a geoid, a line which is perpendicular to the geoid and
passing through the selected point is formed. This line, named the geodetic local vertical, is used to define
the following set of geodetic
parameters:
- geodetic altitude - the distance from the selected point to the reference geoid, measured along the geodetic local vertical,
and is positive for points outside the geoid.
- geodetic latitude - measured in the plane of the local meridian from the Earth's true Equator to the geodetic local vertical,
measured positive north from the Equator.
- longitude - measured in the plane of the Earth's true Equator from the Greenwich meridian to the local meridian,
measured positive
eastward.
In the accompanying figure the selected point is the orbiter, and the geodetic local vertical is the line which is perpendicular
to the geoid and passing through the orbiter center of gravity.
For reference information, the following parameters are also defined in the geodetic coordinate system:
- geocentric latitude - measured in the plane of the local meridian
from the Earth's true Equator to the line that connects the geometric center
of the coordinate system to the point where the geodetic local vertical
intersects the surface of the geoid.
- declination - measured in the plane of the local meridian from the Earth's true Equator to the center of coordinate system/Space
Shuttle position radius vector.
